
Vacuum packaging refers to removing air from a packaging bag and sealing it to isolate the food inside from the outside environment.
In a vacuum, the growth of aerobic microorganisms slows down, reducing protein degradation and fat oxidative rancidity. Furthermore, vacuum packaging promotes the proliferation of lactic acid bacteria and anaerobic bacteria, lowering the pH to 5.6–5.8, further inhibiting the growth of other bacteria and extending the product's shelf life. Vacuum packaging generally needs to be combined with other commonly used preservation methods to achieve good preservation results, such as dehydration, adding spices, sterilization, and freezing.
1. Vacuum packaging can extend the shelf life of food because the air inside is scarce, creating a low-oxygen environment where microorganisms cannot survive, thus keeping the food fresh and less prone to spoilage.
2. Vacuum packaging provides pressure resistance, gas barrier properties, and freshness preservation, effectively maintaining the original color, aroma, flavor, shape, and nutritional value of food for a longer period. However, many foods are not suitable for vacuum packaging and must be packaged using vacuum gas-flushing packaging. Foods that are fragile, easily clump together, prone to deformation and oil leakage, or have sharp edges or high hardness that could puncture the packaging are suitable for vacuum packaging. After vacuum packaging, the pressure inside the bag is greater than the atmospheric pressure outside, effectively preventing the food from breaking or deforming under pressure without affecting the appearance or printing of the packaging.
3. A variation of vacuum packaging is gas-filled packaging. Gas-filled packaging involves filling the bag with a single gas such as nitrogen, carbon dioxide, or a rare gas, or a mixture of two or three gases, after the initial vacuum is created. Nitrogen is a chemically stable gas that protects the product from oxidation and other external interferences, and maintains positive pressure inside the bag to prevent the packaging from being crushed and the product from being damaged. Carbon dioxide dissolves in various fats or water to form weakly acidic carbonic acid, which helps control the activity of molds, bacteria, and other microorganisms.

Vacuum packaging technology originated in the 1940s. In 1950, polyester and polyethylene plastic films were successfully used for vacuum packaging, after which vacuum packaging developed rapidly.
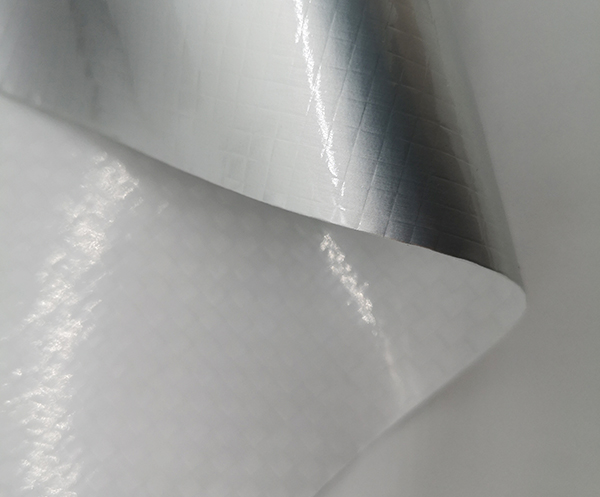
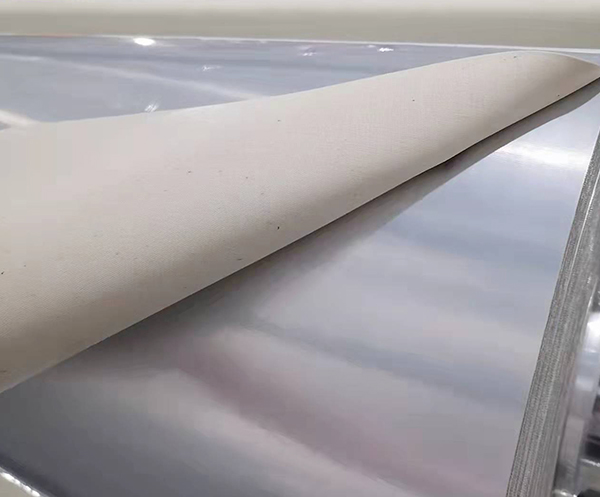
Vacuum aluminum foil cloth: Protective Material for industrial equipment transportation and Storage
Vacuum aluminum foil cloth is a high-performance protective material made by vacuum laminating aluminum foil onto fiberglass or polyester woven fabric. Combining high barrier properties, anti-aging, and wear resistance, it provides superior protection for industrial equipment during transportation and storage. This description contains no company promotion.
Excellent Barrier Properties: The aluminum foil layer completely blocks moisture, oxygen, corrosive gases, and ultraviolet light. This prevents metal components from rusting, protects precision elements from oxidation, and avoids surface aging of coatings or plastic parts due to sunlight exposure.
Durable and Strong: The woven fabric substrate provides high tear resistance and puncture strength. It withstands scratches from edges, stacking pressure during transport, and friction in storage environments, maintaining the integrity of equipment appearance and structure.
Outstanding Weather Resistance: Capable of withstanding extreme temperatures from -40°C to 120°C, it is suitable for multi-modal transport and outdoor storage applications.
During transportation, it can be formed into sealed covers or container liners to protect equipment from sea salt spray and humid air. For storage, it serves as a dust-proof and moisture-proof cover, providing a stable environment for long-term storage of heavy machinery, electronic instruments, and precision equipment. The material is lightweight, heat-sealable, and customizable in size. Optional anti-static and flame-retardant coatings can be applied to meet diverse industrial equipment protection requirements.
Usage Tips: For equipment with sharp edges, use cushioning materials to prevent puncturing the aluminum foil layer and ensure the protective performance is maintained.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
1. How effective is vacuum aluminum foil in preventing moisture and rust?
The aluminum foil layer of vacuum aluminum foil effectively isolates moisture, oxygen, and corrosive gases, while reflecting ultraviolet rays and heat radiation, preventing rust on metal parts and oxidation of precision components. Its high barrier properties ensure that equipment remains in a dry and stable environment during transportation and storage.
2. How much mechanical damage can it withstand during transportation?
The base material is made of fiberglass cloth or polyester woven fabric, which has high tear resistance, puncture resistance, and compression resistance. It can effectively resist scratches from sharp edges, stacking compression, and handling friction during transportation, protecting the appearance and structural integrity of the equipment. It is especially suitable for long-term transportation of heavy machinery and precision instruments.
3. Can vacuum aluminum foil be customized in size or function?
Yes. The material can be customized in size and thickness (generally 0.08–0.2mm) according to equipment specifications, and heat sealing splicing is supported. Antistatic, flame-retardant, or other special functional coatings can be added as needed to adapt to different industrial equipment and special transportation and storage environments.
4. What are the advantages compared to ordinary plastic film or Aluminum Foil Bags?
Vacuum aluminum foil cloth is superior to ordinary plastic film or aluminum foil bags in terms of moisture protection, corrosion protection, UV protection, and mechanical protection. It not only has stronger barrier properties and higher tear resistance, but also forms a sealed protective layer, reducing the risk of equipment damage during transportation and storage and extending equipment lifespan.
5. What are the precautions for use and recycling?
When using, select the appropriate thickness according to the weight of the equipment and the characteristics of its edges and corners, and use cushioning material on sharp parts to prevent punctures to the aluminum foil layer. After disposal, it should be recycled according to environmental standards. Some products can be recycled and reprocessed, meeting green industrial packaging requirements and reducing environmental impact.
This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.